The Material Comparison of Vacuum Stainless Steel Flasks
2025-06-25
Vacuum stainless steel flasks have become a staple in daily life due to their practical ability to maintain beverage temperatures over extended periods. Whether used for hot coffee on a winter morning or ice water during summer activities, these flasks offer a dependable solution for temperature control and portability. One key factor that affects the performance, safety, and durability of these products is the type of materials used in their construction.
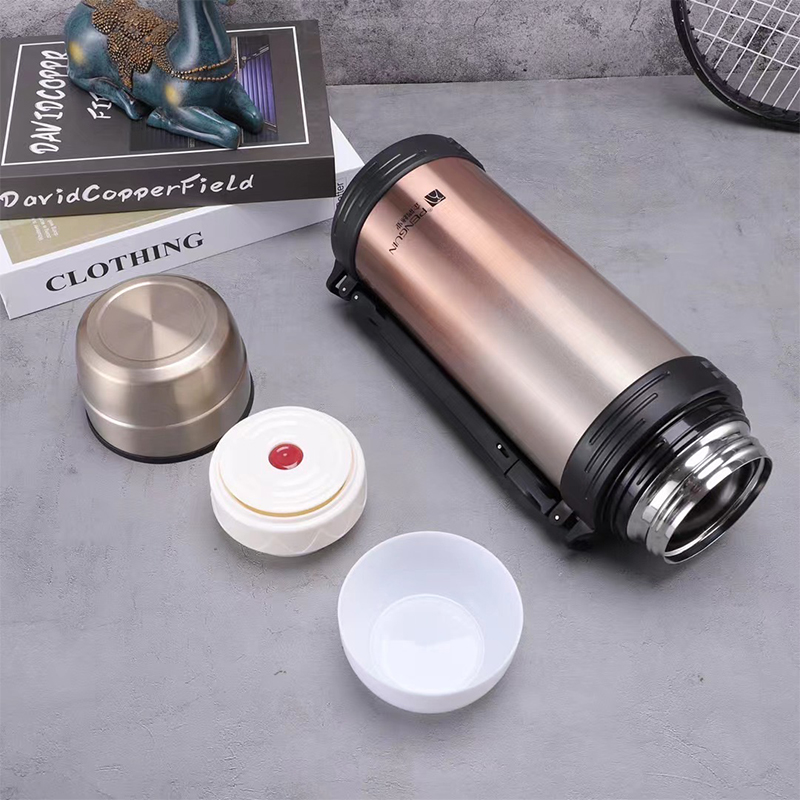

The primary material used in vacuum flasks is stainless steel, chosen for its corrosion resistance, durability, and non-reactive properties. However, not all stainless steel is the same. Different grades vary in composition and performance.
a. 304 Stainless Steel (18/8)
This is one of the commonly used materials in high-quality flasks. The designation "18/8" refers to its composition: 18% chromium and 8% nickel. This alloy offers resistance to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for beverage containers. It is also less likely to retain odors or flavors from previous contents, ensuring a cleaner drinking experience over time.
Advantages: Durable, corrosion-resistant, food-safe, widely used.
Disadvantages: Higher cost compared to lower-grade steel.
b. 316 Stainless Steel (18/10)
Known for its enhanced resistance to saline or chlorinated environments, 316 stainless steel includes 2-3% molybdenum in its composition, which increases its corrosion resistance even further. This grade is typically found in medical instruments and marine applications but is also used in premium flasks aimed at users with specific health concerns or those requiring performance.
Advantages: corrosion resistance, good for acidic or salty contents (like lemon water or soup).
Disadvantages: Higher cost; often only used in inner lining due to expense.
c. 201 Stainless Steel
This is a lower-cost alternative that substitutes manganese for some of the nickel content. It can still provide basic durability and resistance to corrosion, though to a lesser degree than 304 or 316 grades. Some budget-friendly flasks may use 201 stainless steel for external walls while maintaining a 304 inner lining.
Advantages: Affordable and still functional for light use.
Disadvantages: More prone to rust over time, especially in humid or coastal environments; less durable under frequent use.
While stainless steel itself is often sufficient, some vacuum flasks incorporate additional coatings or liners for specific purposes.
a. Copper Plating
Some high-performance flasks feature a copper-coated inner wall between the double layers of stainless steel. Copper improves thermal reflection, enhancing the insulation effect and helping beverages stay hot or cold longer.
Advantages: Improved thermal performance.
Disadvantages: Not in direct contact with beverages; adds cost to manufacturing.
b. Ceramic Inner Coating
A growing number of flasks use ceramic linings over stainless steel to prevent metallic taste and preserve the natural flavor of beverages. This is particularly appreciated by tea drinkers and others sensitive to subtle taste differences.
Advantages: Maintains flavor purity, resists odor retention.
Disadvantages: Can be more fragile; susceptible to cracking if dropped.
Though the core of a vacuum flask is metal, functional components like lids, seals, and mouthpieces often incorporate plastics and silicone.
Food-grade polypropylene (PP) is commonly used for caps and lids. It is lightweight, BPA-free, and relatively resistant to heat.
Silicone is used in seals and gaskets to prevent leaks. It is flexible, durable, and typically non-toxic.
Care must be taken to ensure that these parts are manufactured from certified, food-safe materials, as they do come into contact with hot or cold beverages. Manufacturers that comply with food safety standards such as FDA, LFGB, or EU directives provide more assurance regarding safety.



 English
English  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch